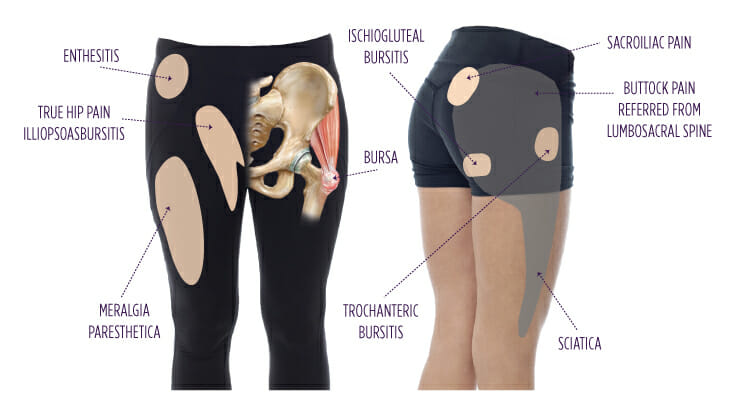
What is trochanteric bursitis?
The bursa is a sac filled with lubricating fluid, located between tissues such as bone, muscle, tendons, and skin, that decreases rubbing, friction, and irritation. The trochanteric bursa sac is located on the outside of each hip. It sits on top of the greater trochanter and underneath the gluteal muscles and tendons.
A healthy trochanteric bursa allows for the muscles to slide along their bony attachments as you move and walk. If the trochanteric bursa is inflamed, walking and sitting can be very painful. This condition is called trochanteric bursitis.
What causes trochanteric bursitis?
Trochanteric bursitis can be caused by an acute injury, prolonged pressure on the affected area, or activities that require repeated twisting or rapid joint movement, such as jogging or bicycling long distances. These activities may lead to irritation or inflammation within the bursa.
Other causes of trochanteric bursitis may be:
- Disc disease of the low back or arthritis of the hip
- Previous hip surgery
- Leg-length inequality
- Improper walking technique due to minor injury or strain
- Overuse of gluteal muscles
- Flat feet or poor shoe choices
- Tight hip or leg muscles
- Spine disease, such as scoliosis, arthritis of the lumbar (lower) spine, and other spine problems
- Bone spurs or calcium deposits
What are the symptoms of trochanteric bursitis?
Symptoms of trochanteric bursitis include:
- Pain on the outside of the hip
- Sharp pain that progresses to a dull ache
- Pain that makes activity and sleep difficult
- Worsening pain when getting up out of a chair, using stairs, and during extended walking, running, or biking
How is trochanteric bursitis diagnosed?
The diagnostic process starts by talking with you about your symptoms and conducting a detailed physical examination. Diagnostic imaging, including X-rays and MRI scans, can be useful for a diagnosis as well.
How is trochanteric bursitis treated?
Most people experience relief from hip bursitis with conservative, nonsurgical treatment. Based on the severity of symptoms, treatment options may include:
- Anti-inflammatory medication
- Cortisone injections
- Orthotics
- Physical therapy
If nonsurgical treatment is not effective, surgery may be appropriate.
What can I do at home to treat trochanteric bursitis?
Home treatment for bursitis includes:
- Rest
- Ice packs to the affected area
- Anti-inflammatory medications to relieve pain and swelling
- Weight loss, to reduce pressure on the hip
- Exercises for the hip and lower back
- Avoiding activities that cause pain