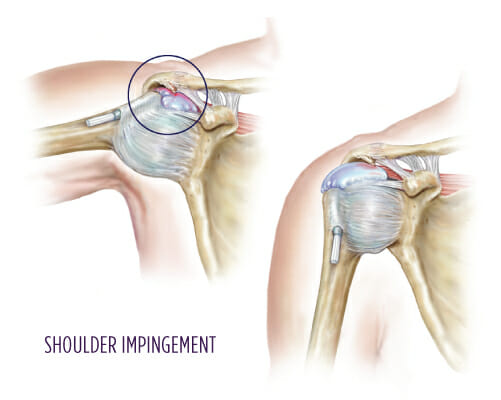
What is shoulder impingement?
The rotator cuff tendons and bursa reside in the narrow space between the top of the upper arm bone (humerus) and the top of the shoulder blade (acromion). When the arm is relaxed at your side, there is enough space. But when the arm is moved away from the body, the space gets narrower.
In a healthy shoulder, this narrowing, or compression, does not cause any pain or irritation. In an unhealthy shoulder, this compression can cause irritation, resulting in pain and inflammation. The inflammation and swelling take up more space, causing symptoms to continue. This is called shoulder impingement.
Learn more about shoulder anatomy
What are the symptoms of shoulder impingement?
Symptoms of shoulder impingement vary widely from person to person. Common symptoms of shoulder impingement include:
- Pain along the front and outside of the shoulder
- Pain with certain activities and in certain positions
- Weakness with certain movements and activities
- Painful clicking and/or popping sensations
- Pain at night
How is shoulder impingement diagnosed?
The diagnostic process starts by talking with you about your symptoms and conducting a detailed physical examination. Diagnostic imaging, including X-rays and MRI scans, can be useful for a diagnosis as well.
How is shoulder impingement treated nonsurgically?
In many cases, shoulder impingement can be treated nonsurgically. The goals of treatment are to relieve pain, restore strength, and increase mobility in the involved shoulder. Nonsurgical treatment options include:
- Anti-inflammatory medication
- Steroid injections
- Physical therapy
What are the surgical treatment options for shoulder impingement?
If a nonsurgical approach doesn’t provide satisfactory function, arthroscopic surgery may be necessary to relieve the symptoms of shoulder impingement. Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows your orthopedic surgeon access to the inside of your joint through several tiny incisions. Your physician can confirm your diagnosis and repair any injured tissue by using a camera and tools inserted into the joint space.
Learn more about shoulder arthroscopy
